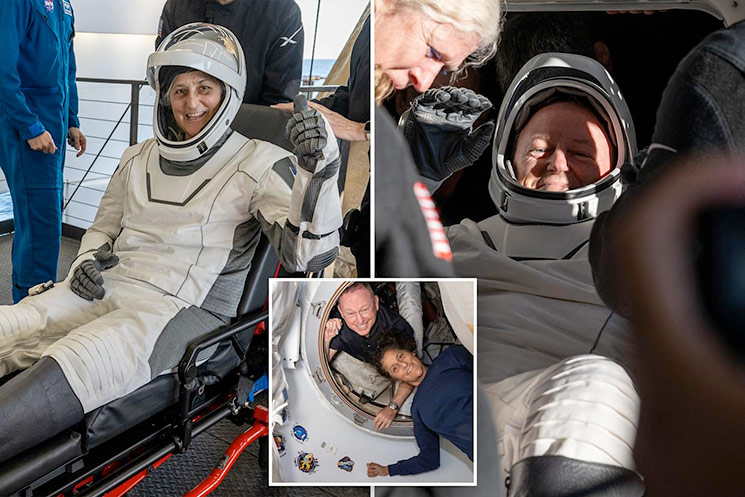
NASA astronauts Suni Williams and Butch Wilmore were stranded in space for 9 months until their dramatic rescue this week.
Williams, 59, and Wilmore, 62, were rescued from the International Space Station (ISS) when Elon Musk’s SpaceX sent a Dragon crew to dock with the ISS and bring them back home.
The two frail astronauts spent a total of 286 days in space.
Musk offered to bring them home in September, but the Biden administration reportedly refused because they didn’t want then-candidate Donald Trump to get all the credit.

A Dragon capsule carrying Williams and Wilmore splashed down off the coast of Tallahassee, Florida just before 6 p.m. on Tuesday.
While they were lost in space, Williams and Wilmore’s weekly paychecks were direct deposited into their bank accounts.
Astronauts have a base salary of between $125,000 and $163,000 per year, according to the Washingtonian.
How much overtime did the 2 astronauts earn while they were abandoned in space?
The Washingtonian spoke to former astronaut Cady Coleman who said that an astronaut’s salary is structured differently from traditional overtime pay. She said they’re paid like any other federal worker on a business trip.
“For me, it was around $4 a day,” she said — that was back in 2010. They get paid a little bit more now. The federal travel allowance is $178 per day.
Coleman said they get paid extra for housing and food while traveling on the road. “There is some small amount of money per day for incidentals that they end up being legally obligated to pay you,” she explained.
Coleman said Williams and Wilmore could expect to earn roughly $1,148 each on top of their salaries.
If they get the higher per diem rate for travel, they’d receive an additional $51,000 each for their time spent lost in space.
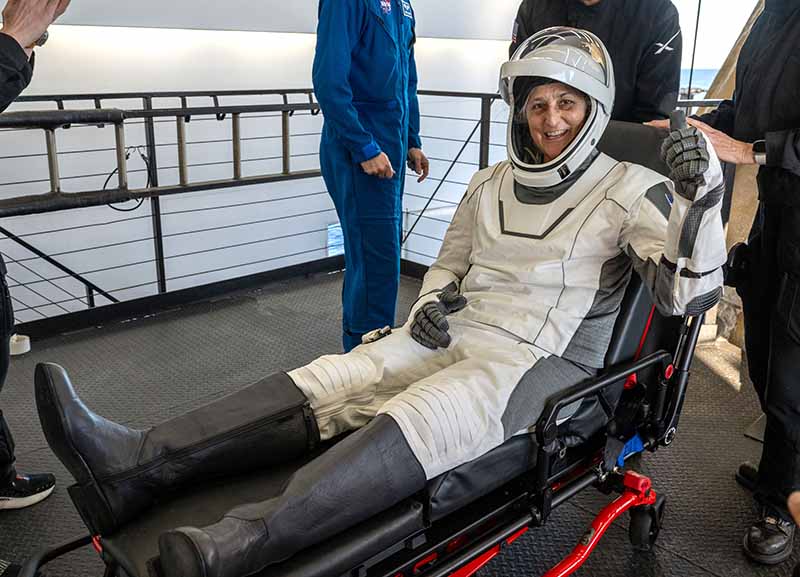

Williams and Wilmore will spend the next 6 weeks in a specialized rehab program to learn how to walk again.
They will also be monitored for cardiac problems since their hearts have to work harder back on Earth.
In addition, they risk blood clots due to increased blood volume and the effects of Earth’s gravitational pull.