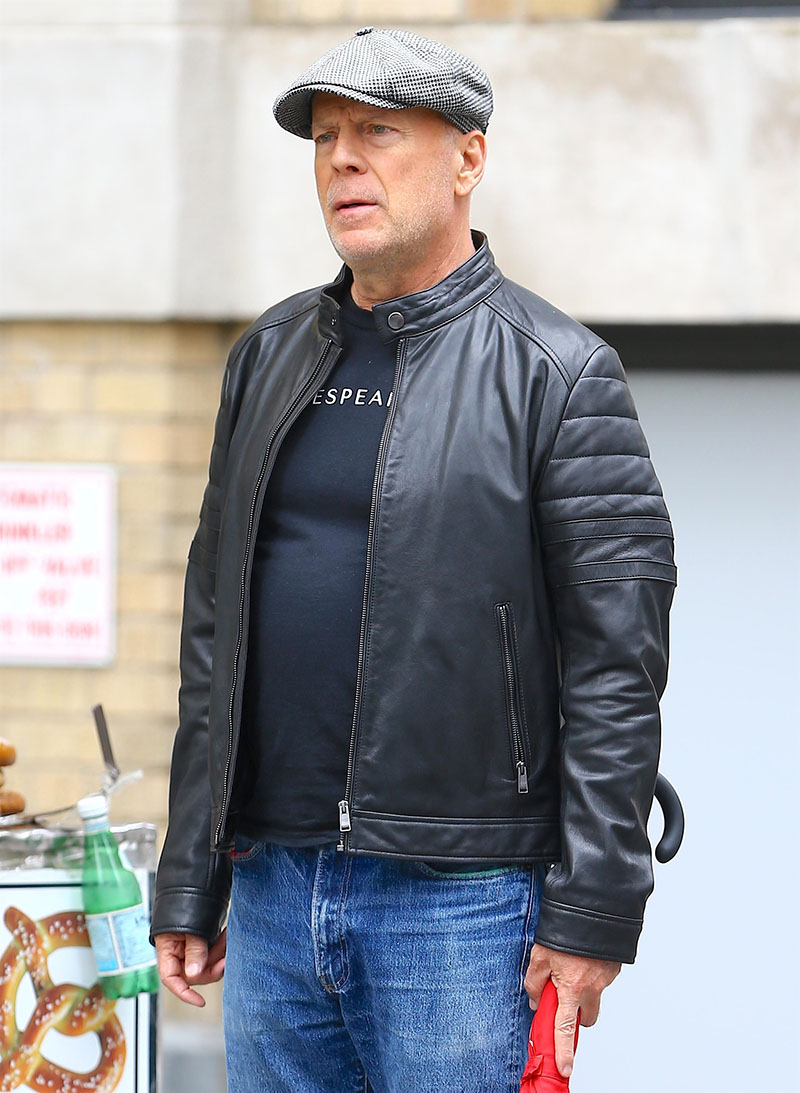
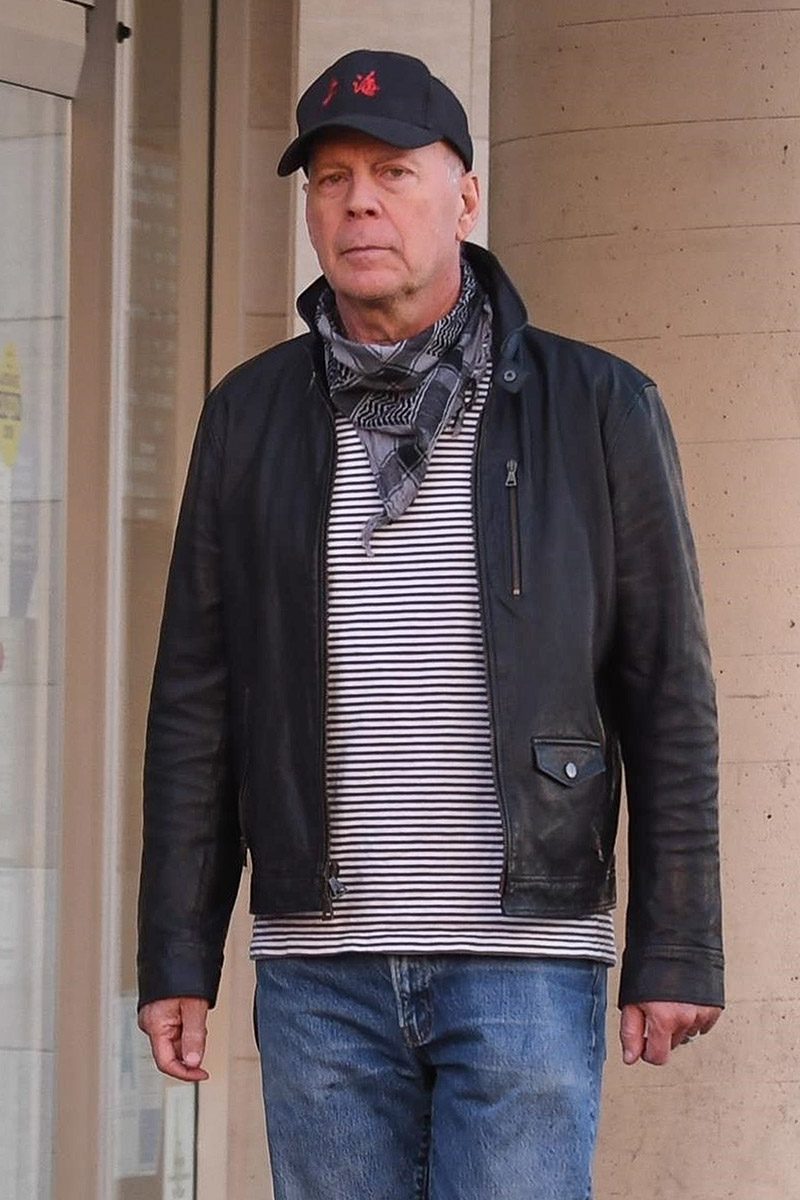
Bruce Willis has been diagnosed with a neurological disorder called aphasia, which affects the area of the brain that controls speech.
The 67-year-old actor will take a hiatus from acting, his family said in a statement on Wednesday. The statement did not reveal the cause or severity of his aphasia.

In a statement on social media, his family said:
“To Bruce’s amazing supporters, as a family we wanted to share that our beloved Bruce has been experiencing some health issues and has recently been diagnosed with aphasia, which is impacting his cognitive abilities.
“As a result of this and with much consideration Bruce is stepping away from the career that has meant so much to him. This is a really challenging time for our family and we are so appreciative of your continued love, compassion and support. We are moving through this as a strong family unit, and wanted to bring his fans in because we know how much he means to you, as you do to him.”
What is Aphasia?
Aphasia is a neurological disorder that affects the part of the brain that controls speech. Causes include stroke, tumors or head trauma, brain infections, or neurodegenerative diseases.
Aphasia affects a person’s ability to speak clearly. Patients may mix up words – spoken or written – or they may jumble their words in a nonsensical way (word salad).
Patients usually don’t realize that their speech is confusing to other people.
Aphasia can also cause problems with writing, understanding speech and listening to speech.
He is best known for his films including the Die Hard franchise, The Sixth Sense, Armageddon, Pulp Fiction, and Sin City.
Willis initially went into acting to control a stutter speech impediment.
Causes of Aphasia
Strokes are the most common cause of aphasia, followed by head trauma, tumors, brain infections, or neurodegenerative diseases.
According to the National Aphasia Association, aphasia affects about 2 million people in the United States. People diagnosed with aphasia are typically middle-age or older.
Symptoms of Aphasia
Symptoms of aphasia depend on the severity of damage to the brain. Patients will have difficulty expressing and enunciating words and sentences, and/or difficulty understanding spoken language.
- speaking in short, incomplete sentences or phrases
- speaking in sentences that others can’t understand (jumbled speech)
- using the wrong words or nonsense words (word salad)
- using words in the wrong order, mixing up words
Patients also have problems understanding spoken language or keeping up with fast paced language.
Treating Aphasia
Treatment for aphasia includes speech therapy, group therapy to practice communication skills, learning to use other forms of communication. Using computers to help form sounds.