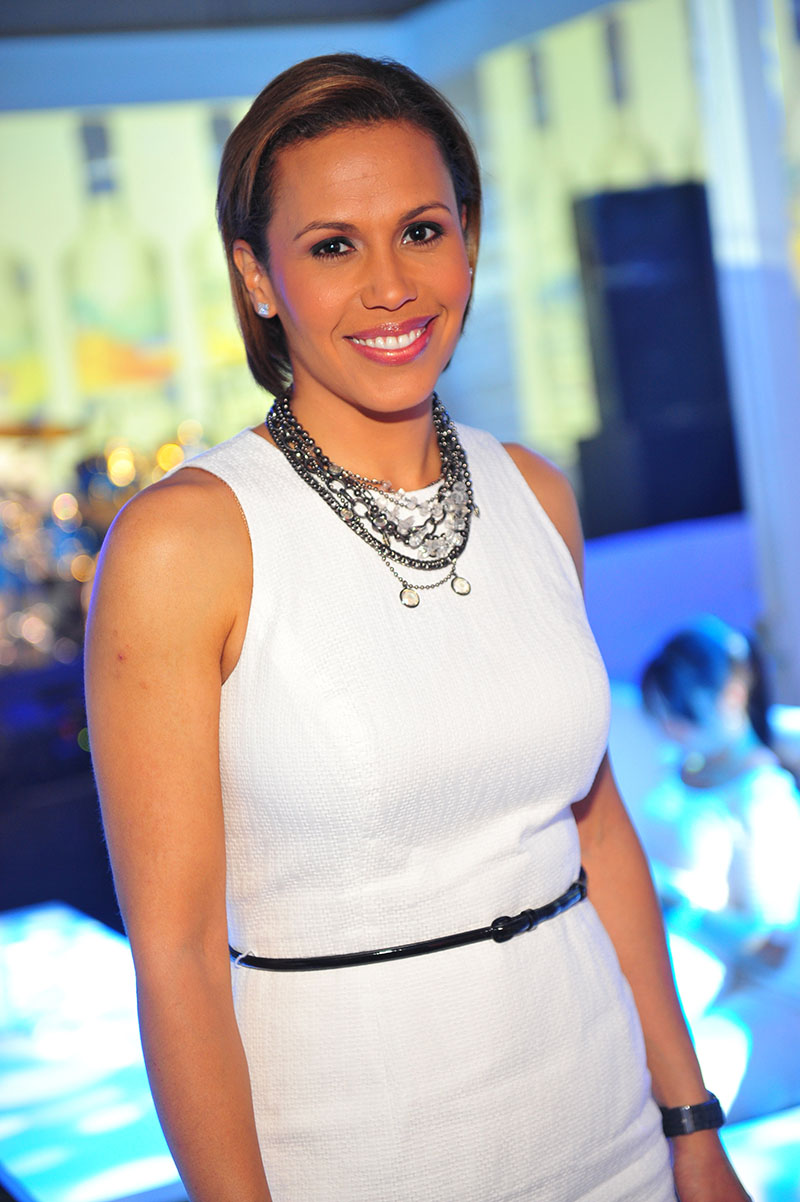
Emmy-winning news anchor Jovita Moore underwent surgery to remove two small brain tumors early Friday morning.
Jovita worked as a news reporter and anchor at Channel 2 Action News for two decades.
[Click here to leave your well wishes for Jovita]
Just before going on the air Monday, Jovita told Channel 2‘s Justin Farmer that she wasn’t feeling well.
Later, as she walked through a grocery store parking lot, she felt lightheaded. “I was walking. I remember walking across parking lot and feeling like I wasn’t going to make it to the door. I was walking like in quicksand,” Jovita said.
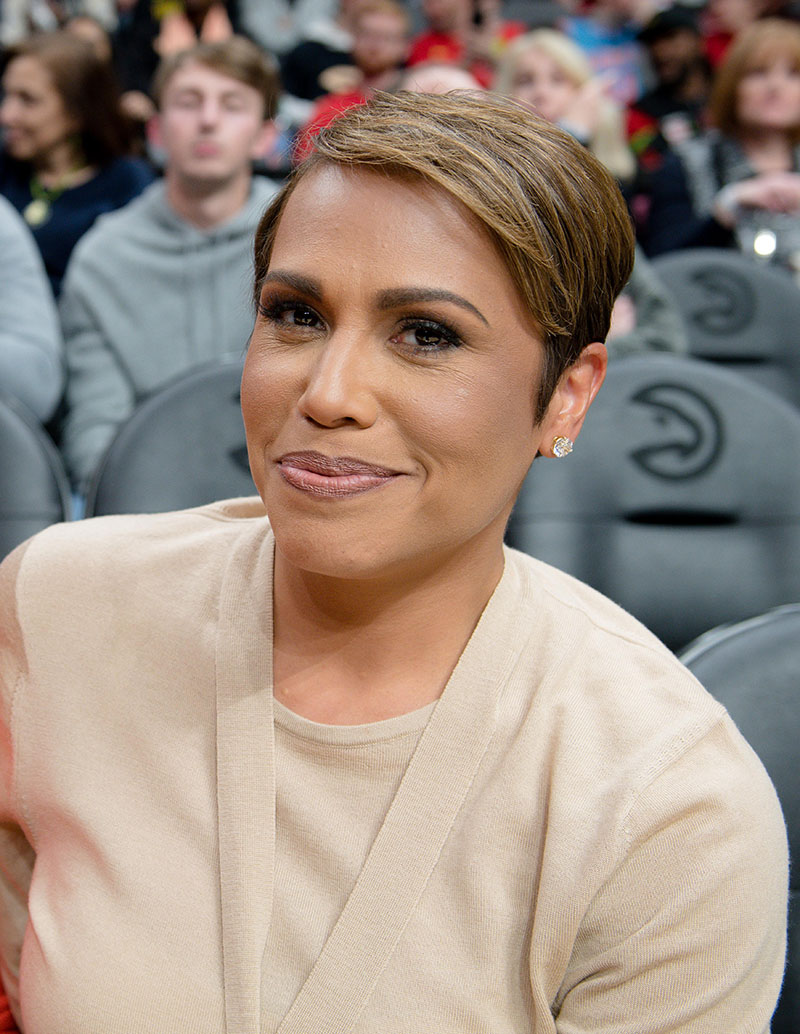

She was rushed to an emergency room, where a brain scan revealed two small brain masses.
Jovita told co-workers she was sometimes “forgetful, disoriented and just not feeling myself.”
What is a Brain Tumor?
A brain tumor occurs when abnormal brain cells clump together to form a mass. As the tumor grows, it presses on the surrounding tissue. Eventually, the pressure on surrounding structures causes symptoms, such as in Jovita’s case.
Brain tumors can remain in the brain or metastasize (spread) elsewhere in the body.
Cancer in other parts of the body, such as the lungs, can metastasize to the brain.
Tumors may be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
What are the risk factors for a brain tumor?
A family history of cancer is one of the risk factors. About 5 to 10 percent of all cancers are hereditary.
Brain tumors are diagnosed more often in Caucasians and biracial, mixed people.
Certain chemicals, such as industrial cleaners, solvents, or medications can increase your risk for brain cancer.
Exposure to radiation can also increase risk.
According to the American Brain Tumor Association, people who never had childhood chicken pox are at greater risk of getting brain tumors.
Signs and symptoms of a brain tumor
Signs and symptoms of a brain tumor depends on the type, size, and location of the tumor within the brain. The space surrounding the brain inside the skull doesn’t allow for much wiggle room. A tumor, or even an aneursym, will press on surrounding tissues causing noticeable signs and symptoms.
Signs & symptoms include:
How are brain tumors diagnosed?
Your doctor will order diagnostic tests and perform a physical exam. The doctor will use an ophthalmoscope to visualize your optic nerves inside your eues. The scope shines a light in your eyes to see if your pupils are unequal or dilated.
Diagnostic tests include CT scan, MRI, angiography and skull X-rays.
How are brain tumors treated?
Treatment depends on the type, size, and location of the tumor. The most common treatment is surgery to remove the tumor.
Surgery can also be combined with chemotherapy and radiation.
There are risks involved with brain surgery, such as loss of mobility, loss of speech and paralysis. Post-surgical infection is also likely.
Patients may temporarily lose the ability to walk or speak after surgery, depending on the location of the tumor that was removed.
Some patients will require physical therapy or speech therapy after surgery.
This has been your Medical Minute.
DISCLAIMER
Any medical information published on this blog is for your general information only and is not intended as a substitute for informed medical advice. You should not take any action before consulting with your personal physician or a health care provider. Sandrarose.com and its affiliates cannot be held liable for any damages incurred by following information found on this blog.